Now, there are two ways to become a Yellowstone National Park Junior Ranger! If you are coming to the park you can pick up a booklet and earn a Junior Ranger badge in person. If you can't make it to the park, however, you can still earn a Virtual Junior Ranger badge right here on our website! To get your virtual badge, explore the following sections and complete each of the activities below. Then, a park ranger will swear you in and you can download your Virtual Junior Ranger badge to show off to your family and friends. Have fun! 
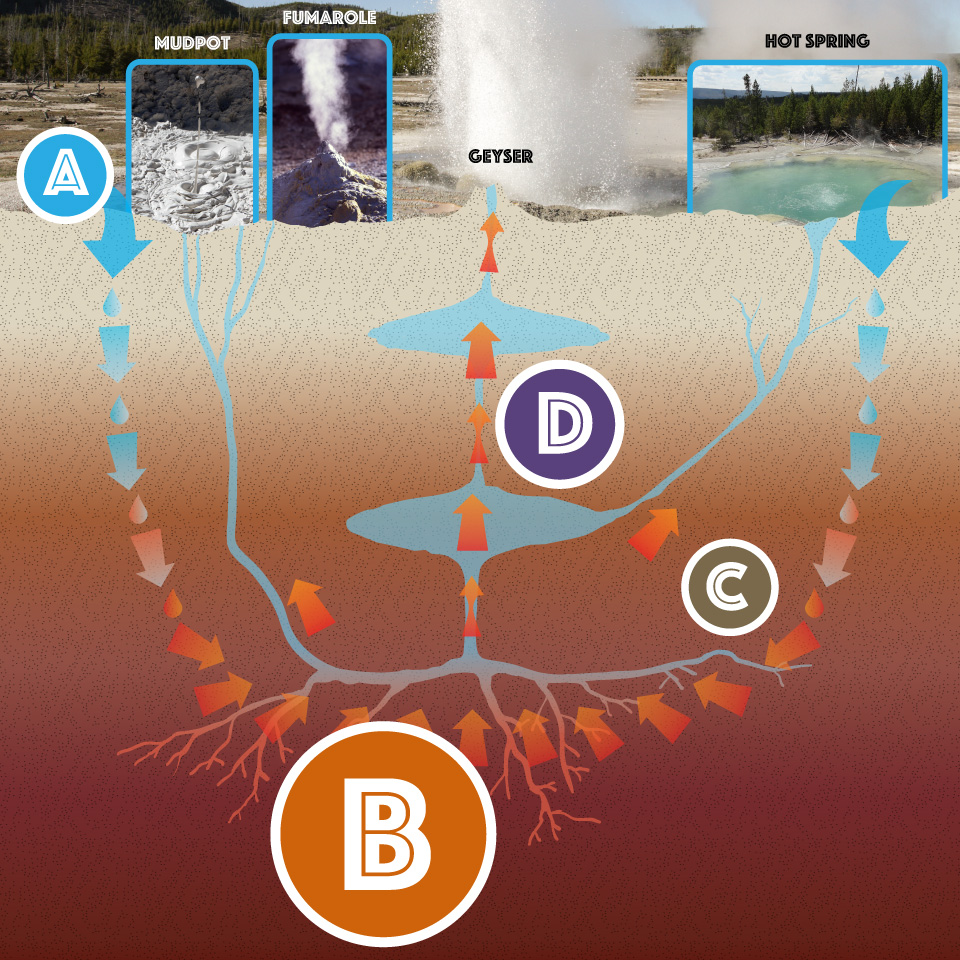
About 631,000 years ago, Yellowstone exploded in a massive volcanic eruption. It blew volcanic ash and gas into the air. As the underground magma reservoir emptied, a giant crater, or caldera, formed. Take a look at what is beneath Yellowstone:
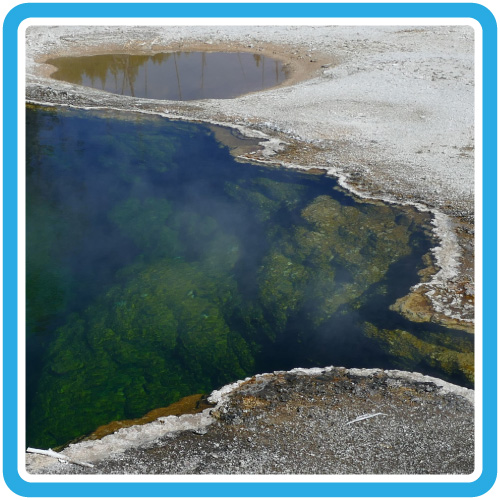
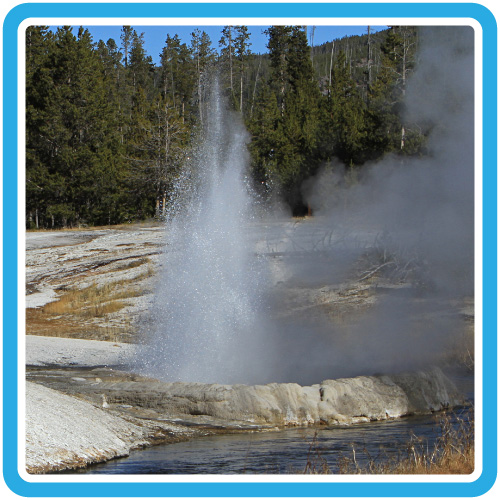
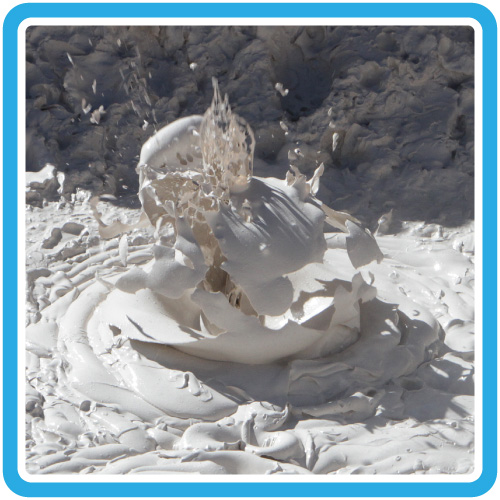
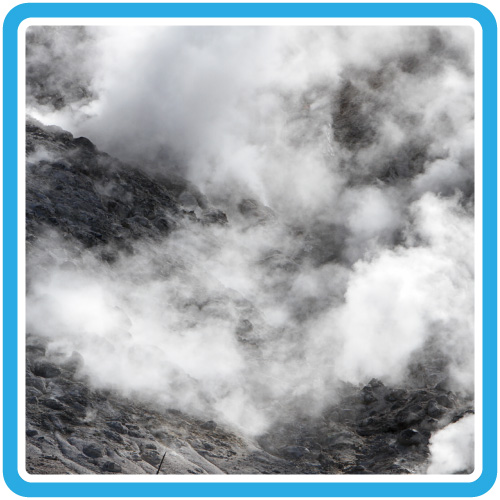
Water heated by magma escapes from the ground through geysers, hot springs, and other hydrothermal features in the park.
►Check it out! Look at the map of ash fallout from the previous three major eruptions. If you live in the US, does your state have ash from the Yellowstone super volcano? 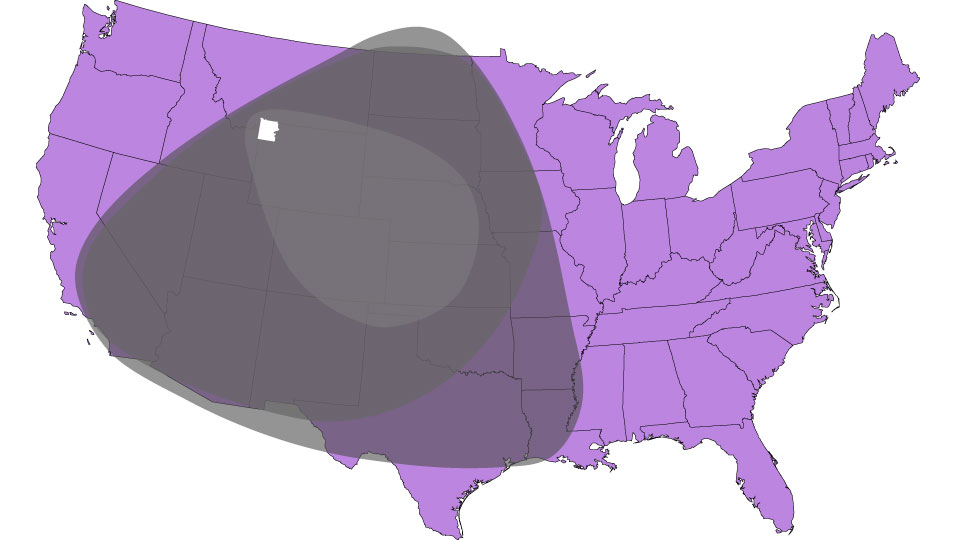
Check out these three major eruptions. Can you guess where the next eruption might happen? 
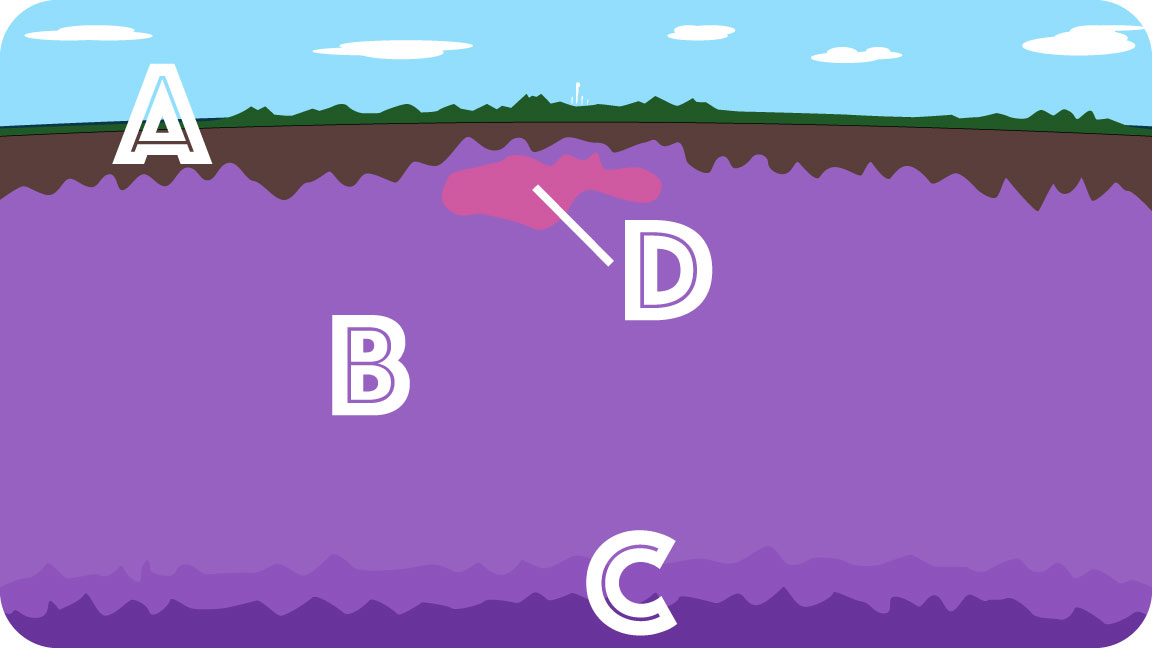
Yes. The heat undeneath the park fuels many of the hydrothermal features. Earthquakes (1,000 to 3,000 per year) reveal activity below ground. The University of Utah Seismograph Stations track this activity closely. Visit the university's seismograph web page to see real-time monitoring data. A caldera is a large depression in the earth that is formed after a volcano erupts and collapses. One of the largest volcanic eruptions known to have occurred in the world created one of the largest known calderas, the Yellowstone Caldera, which is 30 x 45 miles (48 x 72 km) wide. Simulate for yourself how the Yellowstone Caldera was formed. What You'll Need
|
| C. Length of Eruption | D. Interval Until Next Eruption |
|---|---|
| < 3 minutes | 70 minutes |
| > 3 minutes | 101 minutes |
Step 3
Add the start time for the first eruption (A) with the interval number of minutes until the next eruption (D). This is the prediction for the next eruption!
_________(A) + _________(D) = ____________ (Your Prediction!)
Step 4
Return to the Old Faithful Geyser Live-stream Webcam to find the rangers’ prediction for the next eruption: __________ How close is your prediction to theirs? ________________________
Step 5
Watch the next Old Faithful Geyser eruption. When did it start? ________ How did the actual start time compare to your prediction? To the rangers’ prediction? Remember, Old Faithful is a natural feature and changes often, so any prediction may not prove to be exactly right.
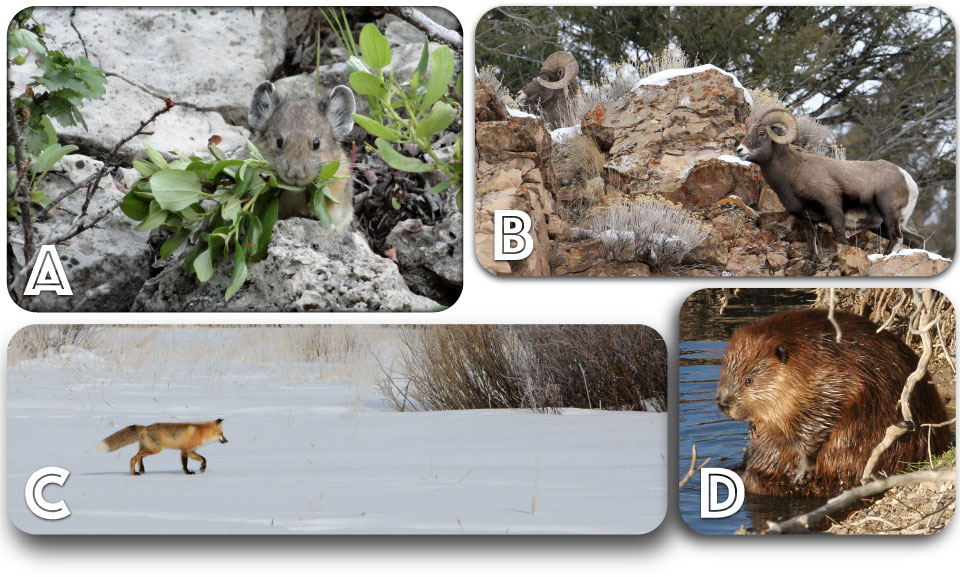


Every animal has a habitat—a place that provides the food, shelter, space, and water it needs to stay alive. Learning about animals and how they live is important to understanding their role in Yellowstone's environment.
- Food (A) is essential. An animal must look for food or eat most of the time it's awake.
- Shelter (B) protects an animal from predators and allows it to rest.
- Space (C) is the room an animal needs to find food, water, and attract a mate.
- Water (D) is needed for drinking, finding food, or just for fun.

Grizzly Bears
- They can run up to 45 miles per hour (72 kph).
- They eat nuts, berries, plant roots, and other animals—making these top predators omnivores.
- They scratch their backs on "rub trees," leaving behind hair that scientists use to learn about bears.

Black Bears
- They are more common than grizzly bears, and are found across North America.
- While they are called black bears, their fur can be brown, blond, or cinnamon in color.
- They have shorter, more curved claws that allow them to climb trees. However, this makes them less capable diggers compared to grizzly bears.

Bison
Yellowstone National Park is the only place in the United States of America where bison have lived continuously since prehistoric times. Yellowstone is also home to the nation's largest bison population on public land.
- Males can weigh 2,000 pounds (907 kg).
- They roam great distances as they continuously eat.
- Their thick winter coats are so well insulated snow can stay on their backs without melting.

Elk
An estimated 10,000 to 20,000 elk live in Yellowstone during the summer season. During the winter, most leave the park.
- They are the most abundant large mammal in Yellowstone.
- Male antlers can weight about 30 pounds (14 kg) per pair and are shed every year.
- Calves are born with white spots to help them hide from predators.

Northern Rocky Mountain Wolves
Wolves are highly social animals and live in packs. Although wolf packs once roamed from the Arctic tundra to Mexico, loss of habitat and extermination programs led to their demise throughout most of the United States of America by early in the 1900s. Today, nearly 100 wolves call Yellowstone home.
- They live and travel in packs of ten animals (on average).
- They communicate through barks, whines, growls, and howls.
- The pack cares for new pups until they can hunt on their own, at about ten months.

Yellowstone Cutthroat Trout
Yellowstone cutthroat trout are the most wide-spread native trout in the park, and are an important food for at least 16 species of birds and mammals. However, their population has declined substantially since the mid-1980s due to the invasion of lake trout into Yellowstone Lake.
- They have a red-orange mark under their jaw.
- They require cool, clean water in streams or lakes.
- They spawn, or lay eggs, in spring and early summer.

As the world's first national park, Yellowstone did not come with a rule book or a manual on how national parks should be run. Things didn't always go well, but we continue to learn and improve the ways we preserve this amazing place.
- In the early days of the park, bears could be fed along roadsides and at garbage dumps. Today, bears in the park find natural food and are wild.
- Opened in 1914, the Geyser Baths Bathhouse was a swimming pool at Old Faithful. Today, we understand how easily hydrothermal systems can be damaged and destroyed.
- Until the early 1900s, all predators were routinely killed in Yellowstone. Today, predators are valued as an important part of Yellowstone's ecosystem.
To preserve Yellowstone, we must all be good stewards. Stewardship means making a difference in our world and trying to make it a better place. Yellowstone's park rangers were once kids, just like you, and have dedicated their lives to protecting special places like Yellowstone.
The arrowhead is the symbol of the National Park Service and what it protects. It is a reminder of the nature and culture national parks protect. Take a look at the arrowhead, then take a look at what each part of the arrowhead represents.

The mountain represents: geology such as mountains, volcanoes, glaciers, arches, dunes, geologic processes, fossils, and so forth.
The sequoia tree represents: vegetation such as trees, cactuses, grasses, wildflowers, aquatic plants, lichen, and so forth.
The bison represents: wildlife such as mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, fish, coral, amphibians, mollusks, and so forth.
The lake represents: water resources such as rivers, lakes, oceans, and shorelines.
The arrowhead shape represents: cultural resources and heritage such as Native Americans, explorers, inventors, artists, American history, and technological advancements.

- Duration:
- 56.223 seconds
Watch this video to get sworn in as a Virtual Junior Ranger completing your Virtual Junior Ranger activities!
Virtual Junior Ranger Pledge
As a Virtual Junior Ranger, I _______________ promise to learn all I can about Yellowstone National Park, and its plants, animals, history, and natural features. I will continue to learn and teach others about how to protect the natural world.

Right click the image above and select "Save As" to save and print your Virtual Junior Ranger badge. After printing it, cut it out and glue it to cardboard or tape it into your passport book!
Last updated: March 21, 2025


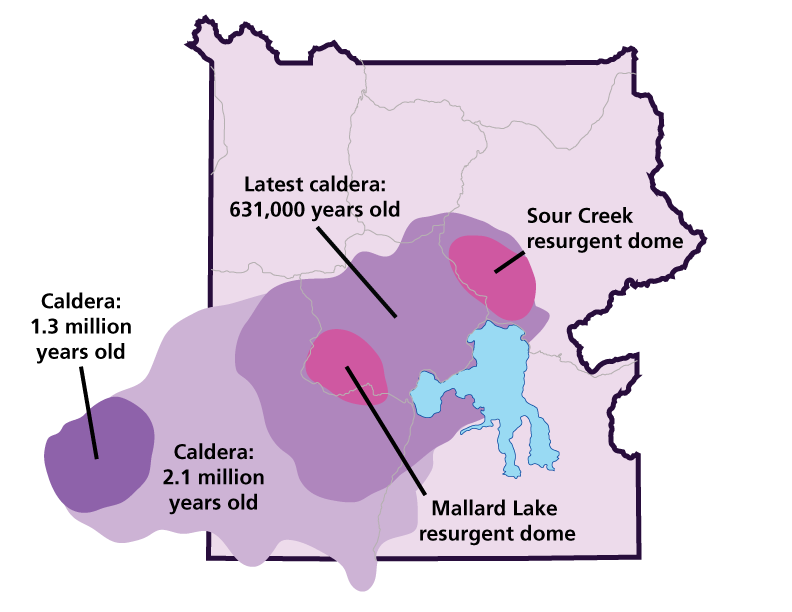 As earth's plates drift, the North American plate slowly moves over the Yellowstone hotspot.
As earth's plates drift, the North American plate slowly moves over the Yellowstone hotspot.