
USGS AVO photograph by Stephanie Prejean
Introduction
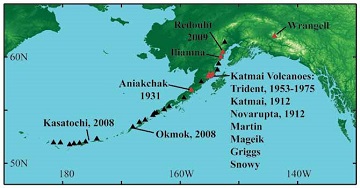
Alaska’s national parks contain 11 historically active volcanoes (Figure 2), which produce thousands of small earthquakes every year. These earthquakes are voices of the magmatic and geothermal systems within the volcanoes. The Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a joint program of the U.S. Geological Survey, the Geo-physical Institute at the University of Alaska Fairbanks, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, monitors volcanic earthquakes year round with networks of seismometers (Figure 4). Data from these networks allow AVO to evaluate the state of magmatic systems and provide warning of volcanic unrest, potential eruptions, and hazards. The key to correctly interpreting earthquakes lies in understanding the physical processes that trigger earthquakes at volcanoes.
Earthquakes Triggered by Magma Ascent
The rise of magma through the Earth’s crust can trig-ger seismicity for many reasons. Ascending magma puts pressure on the surrounding crust, often creating small fractures as rock breaks to accommodate the increased volume (McNutt 2005). In addition, gases released from rising magma (water, carbon dioxide, and others) can further pressurize the surrounding rock, generating earthquakes. For these reasons, earthquake swarms (bursts of many earthquakes closely spaced in time and location) almost always precede volcanic eruptions.
The relationship between seismicity and magma ascent is controlled by many factors including: the chemistry and gas content of the magma, regional tectonic stresses, the temperature of the surrounding crust, the type of rock surrounding the conduit system (e.g., granite vs. sedimentary rock), and whether there are pre-existing faults in the area or an existing, recently occupied conduit to facilitate magma migration. Because of these variables, there is an impressive diversity in seismicity characteristics associated with magma ascent.
For example, prior to the 2008 eruption of Kasatochi volcano (Aleutian Islands), the largest earthquake associated with magma ascent was magnitude (M) 5.8. In contrast, the largest pre-eruption earthquake of the 2009 eruption of Redoubt Volcano was only M 3.1, and the largest pre-eruption earthquake of the 2006 eruption of Augustine Volcano was M 2.1. Some eruptions, such as the 2009 Redoubt eruption, produce strong volcanic tremor (continuous vibration of the Earth’s crust) prior to large explosions, while other volcanoes do not exhibit this type of activity at all. Given this range of seismic behavior, correct eruption forecasts rely on interpreting seismicity in the context of many other data streams, including historical activity at the volcano, the chemistry of magma typically erupted from the volcano, and other clues to magma ascent gleaned from ground deformation, satellite, and gas monitoring data.
Seismic activity in the months leading up to the 2009 eruption of Redoubt Volcano displayed many classic signs of earthquake triggering by magma ascent. Four months prior to eruption onset, earthquakes known as deep-long-period events (DLPs) began occurring in the Earth’s lower crust at 15-22 miles (25-35 km) depth. DLPs radiate lower frequency seismic energy than typical brittle-failure earthquakes and likely result from slugs of magma or other fluids forcing their way upward through rock (see Figure 5 on page 29 for schematic). Thus, these DLPs signaled renewal of magma ascent from lower crustal depths. Three months prior to eruption onset, vigorous shallow volcanic tremor and earthquake swarms began in and below the volcano. This shallow seismicity was likely triggered by pressurization due to injection of magma into the near-surface rocks, release of gases from magma, and heating and boiling of ground water. Earthquake activity increased markedly in the two days prior to eruption (Figure 3), as the final ascent of magma perturbed the sur-rounding rocks. At that time, small earthquakes occurred at a rate of 1-5 per minute. This build up in the number of earthquakes with time is fairly typical for a stratovolcano prior to eruption, although precursory activity at many volcanoes veers from this pattern markedly. Okmok Volcano in the Aleutian Islands, for example, erupted in 2008 with only 60 minutes of elevated seismicity (Larsen et al. 2009). The clear precursory earthquake sequence associated with the 2009 eruption of Redoubt Volcano allowed scientists at AVO to supplement the monitoring network prior to the eruption with additional equipment (Figure 4) and to correctly forecast the eruption.

USGS AVO photograph by Game McGimsey
Earthquakes Triggered by Distant Large Earthquakes
After a large earthquake in Alaska, AVO scientists are frequently asked, “Does that earthquake affect the volcanoes?” The answer to this question is complex and is the subject of ongoing research. In general, large earthquakes in Alaska and around the globe that result from the relative motion of tectonic plates do not cause volcanoes to erupt. However, there are a few cases globally where large regional earthquakes have clearly initiated volcanic activity, such as the 1975 summit eruption of Kilauea Volcano, Hawai’i, following the M 7.2 Kalapana earthquake (Hill et al. 2002).
There is abundant evidence that large earthquakes can trigger small earthquakes (M< 2.0) at volcanoes over amazingly large distances. For example, the 2007 M 8.2 earthquake in the Russian Kurile Islands triggered a small earthquake swarm at Martin Volcano in the Katmai vol-canic cluster, over 2,000 miles (3,500 km) distant (Figure 5). More impressively, the 2004 M 9.2 Sumatra earthquake triggered an 11 minute swarm of small earthquakes at Mt. Wrangell volcano, almost 6,900 miles (11,000 km) distant.
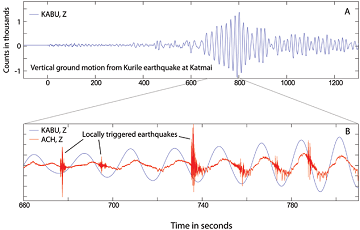
In these and similar cases, local earthquakes were triggered when the highest amplitude seismic waves from the large distant event rolled through the area. This phenomenon, known as remote dynamic triggering, has been observed all over the world (Prejean and Hill 2009). Volcanoes in Katmai National Park and Preserve appear to be particularly susceptible to this type of triggering. Moran et al. (2004) summarize four episodes of remotely triggered seismicity at Martin Volcano in addition to the 2007 example. Generally, these small, triggered earth-quakes do not perturb the volcanic system significantly, nor are they related to movement of magma through the crust. Rather, they can be thought of as earthquakes that might have occurred anyway over the subsequent months. The oscillation of the ground from seismic waves of the distant earthquake simply caused them to occur earlier than they would have otherwise. Moran et al. (2004) inferred that the triggered earthquakes may have resulted from shaking of the shallow hydrothermal system and movement of hydrothermal fluids. Others have argued, however, that the preponderance of remote dynamic triggering suggests that the Earth’s crust is in a state of incipient failure everywhere (Gomberg et al. 2004). That is, rocks in the shallow crust are poised to break, and it only takes a tiny nudge to trigger these small earthquakes in almost any volcanic region.

Photograph courtesy of Gary Freeburg
Ongoing Research
Due to the high earthquake rates and relatively frequent volcanic eruptions in Alaska (one per year on average), many researchers are focusing on volcanoes in Alaska’s national parks to better understand how volcanic earthquakes are triggered. For example, data from a recent seismic experiment in Katmai National Park and Preserve (see Thurber et al., this issue) reveal that many recent earthquakes in the area of Trident and Novarupta volcanoes are likely triggered by increased fluid pressure in a geothermally active region of the Earth’s crust. In another example, Roman and Power (2011) examine earthquake characteristics to infer stress changes in the crust due to magma movement at Iliamna Volcano during a failed eruption (an intrusion of magma into the shallow crust that did not result in an eruption) in 1996-97.
Discriminating between earthquake swarms triggered directly by magma movement and those triggered indirectly by magma (e.g. by high-pressure, magmatically-derived fluids and gases like water and carbon dioxide) is an ongoing challenge at potentially dangerous volcanoes worldwide. We must address this problem to correctly interpret the state of the magma system and resulting volcanic hazards. For these reasons, Alaska’s national parks will continue to be important laboratories for testing and refining our understanding of earthquake triggering at volcanoes.
For more information:
The Alaska Volcano Observatory has a comprehensive web page that includes daily images of activity on seismometers at monitored volcanoes and a database of recent publications.
The USGS Volcano Hazards Program web page provides information about volcanic activity and resulting hazards throughout the U.S.
The Alaska Earthquake Information Center provides information about recent and historical earthquakes in Alaska.
References
Coombs, M., and C. Bacon. 2012. Using rocks to reveal the inner workings of subvolcanic magma chambers in Alaska’s National Parks. Alaska Park Science, this issue.
Gomberg, J., P. Bodin, K. Larson, and H. Dragert. 2004. Earthquake nucleation by transient deformation caused by the M = 7.9 Denali, Alaska, earthquake. Nature 427: 621-624.
Hill, D.P., F. Pollitz, and C. Newhall. 2002. Earthquake-volcano interactions. Physics Today 55: 41.
Larsen, J., C. Neal, P. Webley, J. Freymueller, M. Haney, S. McNutt, D. Schneider, S. Prejean, J. Schaefer, and R. Wessels. 2009. Eruption of Alaska volcano breaks historic pattern. Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union 90 (20): 173-174.
McNutt, S. 2005. Volcano Seismology. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 33: 461-491.
Moran, S.C., J.A. Power, S.D. Stihler, J.J. Sanchez, and J. Caplan-Auerbach. 2004. Earthquake triggering at Alaskan volcanoes following the 3 November 2002 Denali Fault Earthquake. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 94: S300-S309.
Prejean, S.G., and D.P. Hill. 2009. Earthquakes, Dynamic Triggering of. In Encyclopedia of Complexity and System Science, edited by R.A. Meyers. Springer.
Roman, D.C. and J.A. Power. 2011. Mechanism of the 1996-97 non-eruptive volcano-tectonic earthquake swarm at Iliamna Volcano, Alaska. Bulletin of Volcanology 73: 143-153.
Thurber, C., R. Murphy, S. Prejean, N. Bennington. 2012. Earthquake studies reveal the magmatic plumbing system of the Katmai volcanoes. Alaska Park Science, this issue.
West, M., J.J. Sanchez, and S.R. McNutt. 2005. Periodically triggered seismicity at Mount Wrangell, Alaska, after the Sumatra Earthquake. Science 308: 1144-1146.
Part of a series of articles titled Alaska Park Science - Volume 11 Issue 1: Volcanoes of Katmai and the Alaska Peninsula.
Last updated: June 23, 2016
