Last updated: July 9, 2024
Article
NPS Geodiversity Atlas—Kalaupapa National Historical Park, Hawaii
Geodiversity refers to the full variety of natural geologic (rocks, minerals, sediments, fossils, landforms, and physical processes) and soil resources and processes that occur in the park. A product of the Geologic Resources Inventory, the NPS Geodiversity Atlas delivers information in support of education, Geoconservation, and integrated management of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the ecosystem.

Introduction
Kalaupapa National Historical Park (KALA) is located along the north-central coast of the island of Moloka‘i in Maui County, Hawai‘i. Established on December 22, 1980, KALA covers approximately 4,362 hectares (10,779 acres) and contains the site of the Moloka‘i Hansen’s disease (leprosy) settlement, areas relating to early settlement, and a diverse biological community that includes rare and endangered species (National Park Service 2016). The establishment of KALA honors the story of the isolated Hansen’s disease community by preserving its site and values, in addition to telling the Hawaiian cultural history at Kalaupapa that dates back more than 900 years. The landscape of KALA includes the relatively flat Kalaupapa Peninsula (also called the Makanalua Peninsula) with gently sloping flanks of the Kauhakō Crater and three steep-sloped interior valleys whose walls rise to include the rim of some of the steepest sea cliffs in the world. The highest sea cliffs of the north shore of Moloka‘i stand 1,101 m (3,315 ft) above the Pacific Ocean and were designated a national natural landmark because of their geological significance (Thornberry-Ehrlich 2010). The offshore areas of KALA encompass 809 hectares (2,000 acres) and include the islets of Huelo and ‘Ōkala.Geologic Setting
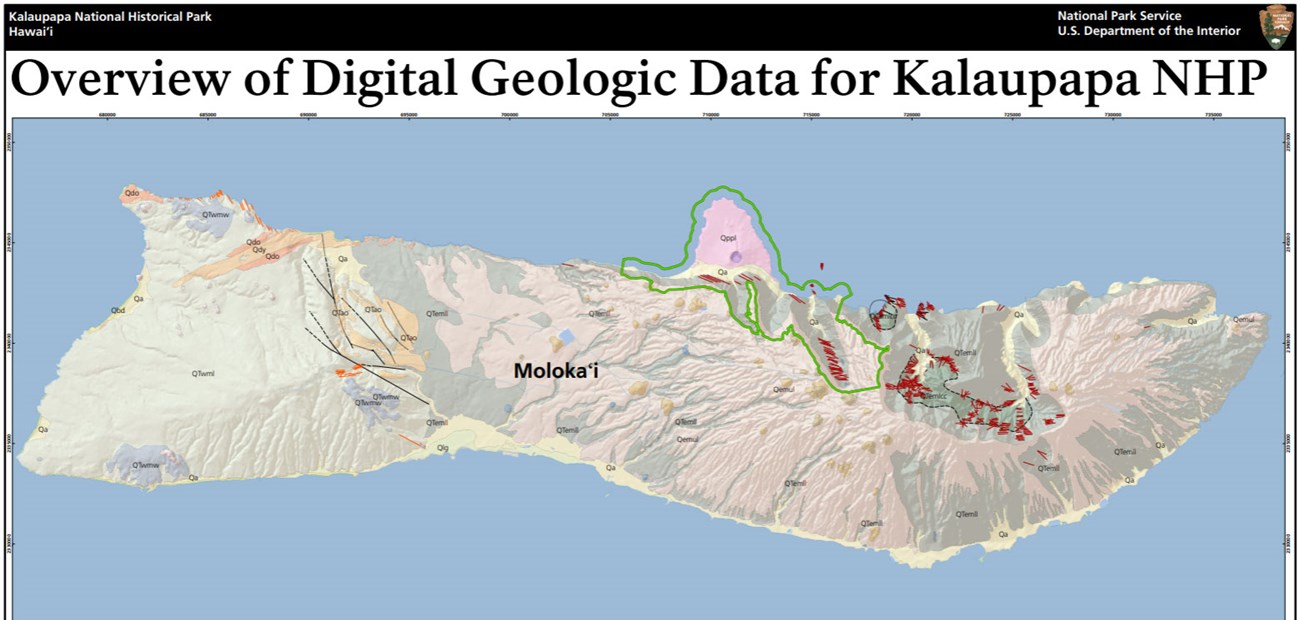
The geology of Kalaupapa National Historical Park is primarily composed of Cenozoic-age igneous units that can be broken down into lava flows, vent deposits, and volcanic domes. The steep sea cliffs that rise above the lower Kalaupapa Peninsula are comprised of the Pliocene–Pleistocene East Moloka‘i Volcanics and represent the oldest exposures in the park. Rocks that form the low-lying tongue of land at the base of the cliffs consist of the Pleistocene Kalaupapa Volcanics. A veneer of Quaternary-age alluvium (unconsolidated sand and gravel deposits) is mapped at the base of the sea cliffs. On the island of Moloka‘i, the East Moloka‘i volcano has its highest peak (Kamakou) at 1,515 m (4,970 ft) in elevation and was once much larger than it is today. At one point in geologic time the northern half of the volcano catastrophically collapsed along a 40 km (25 mi) long scarp, effectively halving the size of the collapse caldera at its summit and forming the famous cliffs (also called pali) of Moloka‘i (Thornberry-Ehrlich 2010).- Scoping summaries are records of scoping meetings where NPS staff and local geologists determined the park’s geologic mapping plan and what content should be included in the report.
- Digital geologic maps include files for viewing in GIS software, a guide to using the data, and a document with ancillary map information. Newer products also include data viewable in Google Earth and online map services.
- Reports use the maps to discuss the park’s setting and significance, notable geologic features and processes, geologic resource management issues, and geologic history.
- Posters are a static view of the GIS data in PDF format. Newer posters include aerial imagery or shaded relief and other park information. They are also included with the reports.
- Projects list basic information about the program and all products available for a park.
Source: NPS DataStore Saved Search 2913. To search for additional information, visit the NPS DataStore.
A NPS Soil Resources Inventory project has been completed for Kalaupapa National Historical Park and can be found on the NPS Data Store.
Source: NPS DataStore Saved Search 2985. To search for additional information, visit the NPS DataStore.
Related Articles
Kalaupapa National Historical Park
National Park Service Geodiversity Atlas
The servicewide Geodiversity Atlas provides information on geoheritage and geodiversity resources and values within the National Park System. This information supports science-based geoconservation and interpretation in the NPS, as well as STEM education in schools, museums, and field camps. The NPS Geologic Resources Division and many parks work with National and International geoconservation communities to ensure that NPS abiotic resources are managed using the highest standards and best practices available.