Last updated: June 14, 2024
Article
NPS Geodiversity Atlas—Casa Grande Ruins National Monument, Arizona
Geodiversity refers to the full variety of natural geologic (rocks, minerals, sediments, fossils, landforms, and physical processes) and soil resources and processes that occur in the park. A product of the Geologic Resources Inventory, the NPS Geodiversity Atlas delivers information in support of education, Geoconservation, and integrated management of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the ecosystem.

Introduction
Casa Grande Ruins National Monument (CAGR) is located approximately 72 km (45 mi) southeast of downtown Phoenix in Pinal County, Arizona. Originally authorized as Casa Grande Ruin Reservation on March 2, 1889, the park unit was redesignated on August 3, 1918. Encompassing about 191 hectares (473 acres), CAGR was established for the preservation and interpretation of the Casa Grande and surrounding features and objects of prehistoric interest (National Park Service 2017a). The Casa Grande (“great house” in Spanish) was named by early Spanish explorers and is a four-story, 18 m (60 ft)-long earthen-walled structure constructed by the Ancestral Sonoran Desert People (Hohokam culture) who inhabited the Gila Valley in the early 13th century. The Casa Grande is the only surviving example of a multi-story, free-standing earthen Great House structure from the Hohokam culture and was built using more than 3,000 tons of local caliche (concrete-like mixture of sand, clay, and limestone) and hundreds of juniper, pine, and other trees used as structural anchors. Besides Casa Grande, CAGR contains 62 documented prehistoric cultural sites, including a ballcourt, platform mound, and irrigation canals that embody one of the most extensive prehistoric irrigation-based agricultural desert societies in North America.Geologic Setting
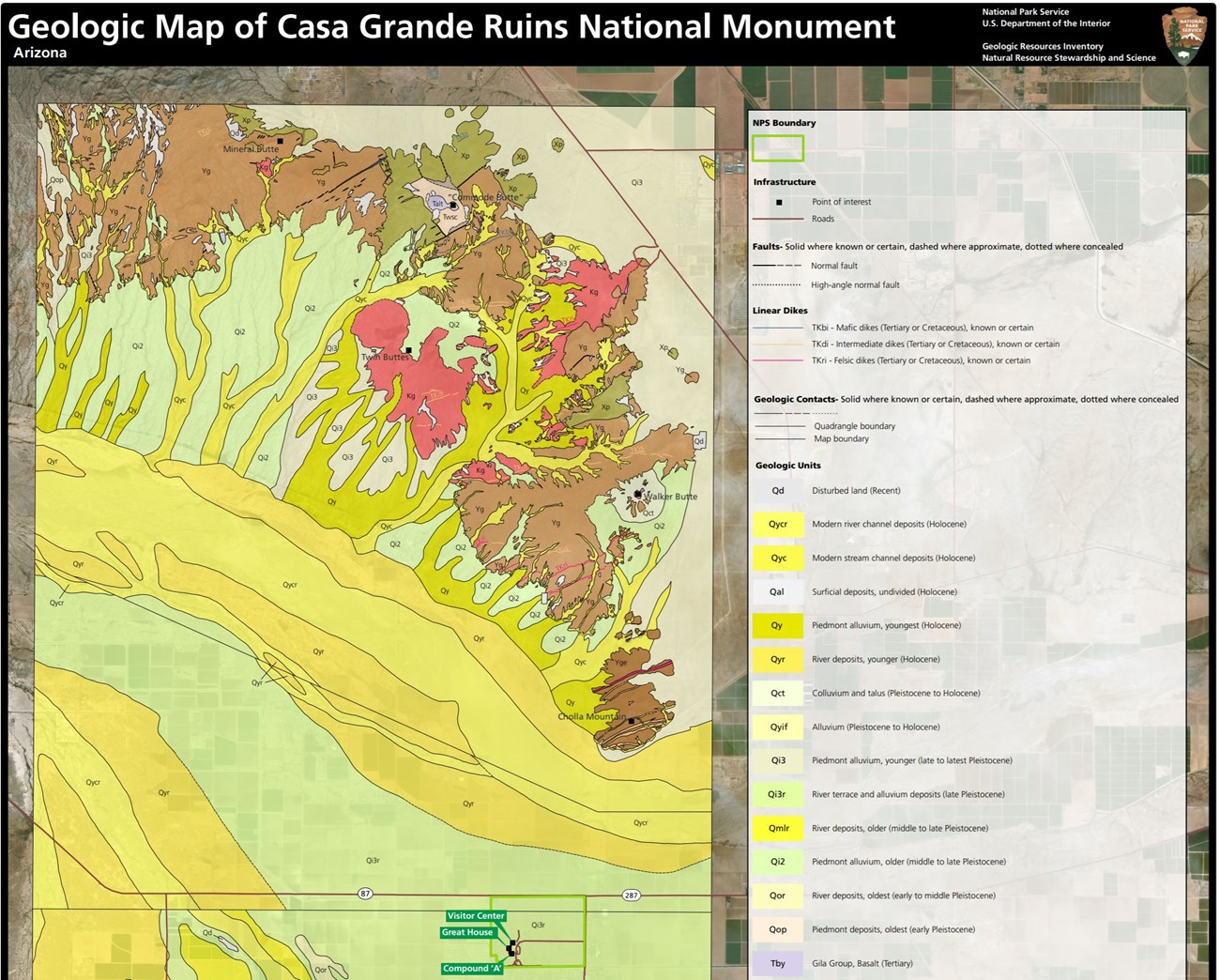
CAGR and the immediate surrounding region are part of the Sonoran Desert sub-province of the Basin and Range physiographic province (KellerLynn 2018). The province is characterized by horst and graben topography where extensional normal faults have created down-faulted structural basins (grabens) separating up-faulted mountain ranges (horsts). CAGR is situated in the down-dropped Picacho Basin. The bedrock geology of CAGR is associated with the history of the Gila River and consists entirely of Pleistocene river terrace and alluvium (unconsolidated gravel, sand, silt, and clay) deposits (Figure 6). The age of the underlying terrace indicates that the Gila River was flowing across the monument area approximately 130,000–10,000 years ago (KellerLynn 2018). Immediately surrounding CAGR are younger Holocene river deposits with localized outcrops of Proterozoic granite to the northeast of the monument.Regional Geology
Casa Grande Ruins National Monument sits near the transition zone of the Colorado Plateaus Physiographic Province—a relatively high, undeformed area—and the Basin and Range Physiographic Province, which is characterized by tilted fault blocks that form long, asymmetrical ranges or mountains and broad, intervening basins. Casa Grande Ruins shares its geologic history and some characteristic geologic formations with a region that extends well beyond park boundaries.
- Scoping summaries are records of scoping meetings where NPS staff and local geologists determined the park’s geologic mapping plan and what content should be included in the report.
- Digital geologic maps include files for viewing in GIS software, a guide to using the data, and a document with ancillary map information. Newer products also include data viewable in Google Earth and online map services.
- Reports use the maps to discuss the park’s setting and significance, notable geologic features and processes, geologic resource management issues, and geologic history.
- Posters are a static view of the GIS data in PDF format. Newer posters include aerial imagery or shaded relief and other park information. They are also included with the reports.
- Projects list basic information about the program and all products available for a park.
Source: NPS DataStore Saved Search 2770. To search for additional information, visit the NPS DataStore.
A NPS Soil Resources Inventory project has been completed for Casa Grande Ruins National Monument and can be found on the NPS Data Store.
Source: NPS DataStore Saved Search 2752. To search for additional information, visit the NPS DataStore.
GRI Geology Image Gallery

NPS Photo.
Related Links