
The pelagic zone, also known as the open ocean, is the area of the ocean outside of coastal areas. Here you will find some of the biggest marine life species. Species here are affected by wave and wind activity, pressure, water temperature and prey. Since, this area spans a large distance animals have to travel far to feed. Sea turtles travel thousands of miles between breeding and feeding grounds. 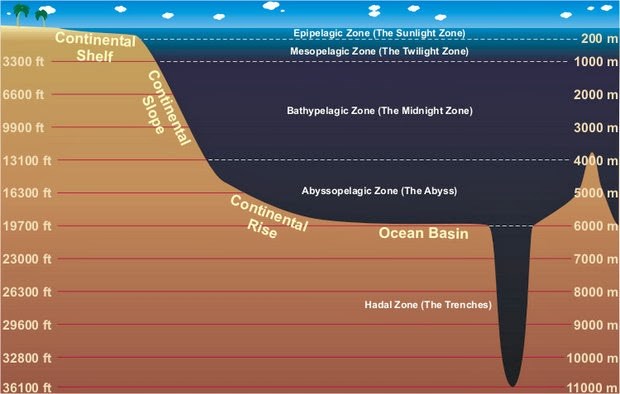
Different Zones within the Pelagic Zone The open ocean lies over the continental shelf. The seafloor is not included in the open ocean.
Learn More |
Last updated: May 13, 2016
